Sustainable waste management is one of the main aspects of a green economy. A green economy is aimed at reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities.
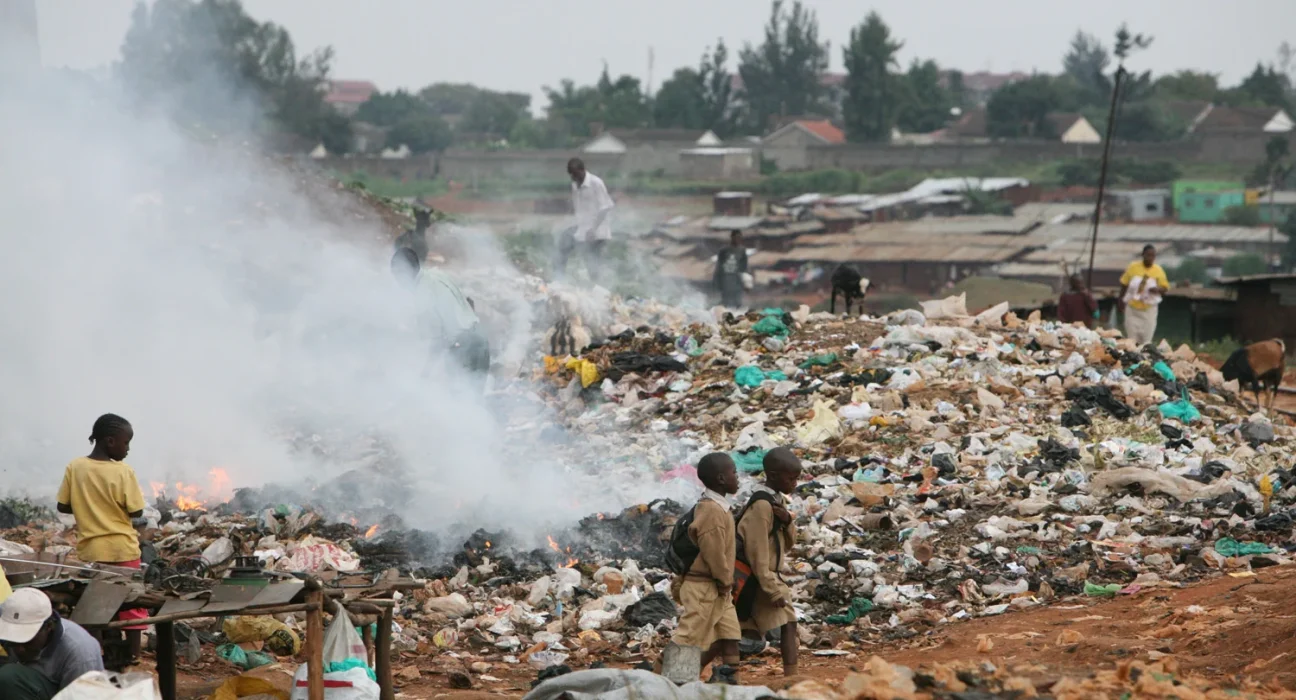
However, production of solid waste in Kenya is increasing by the day with the rapid population growth due to the expansion of the industrial (service and manufacturing) sector especially in urban areas. This is especially the case in Nairobi County where about 2475 tons of solid waste is produced per day.
Waste management is therefore a big challenge. It is hence vital that especially Nairobi has an effective solid waste management system that can be echoed by other public and private organizations.
The goal of this research is using GIS and ICT knowledge in designing, developing and implementing an intelligent and interactive web-based system that would aid in dynamic waste management for Kimathi sub location. This is through depicting its current situation by mapping the existing waste collection, sorting, and dumping locations in the area; identification of optimal locations for collection points in the sub location; implementation of a routing system for the waste management and integrating these different modules into an interactive dashboard for easy access, communication and interaction.
Assessment of the current waste management system especially collection and disposal of waste in the area was done. These findings mainly acquired through GIS technology were manipulated and analyzed through the same and was coupled with web technology to enable increased performance of the system, cost reduction and involvement of citizens in waste management. Digital technology has also been brought to play in connecting different components of the system into one interactive dashboard.
A suitability map produced in this research is key since it can enable planners and policy makers to determine the fitness of the position of a collection point/ bin in the area. Depicted from the results is a case where most of the sub location is not suitable to set up waste collection points, further pointing out the need of such analysis/ findings to help minimize or completely eradicate the emergent dump spots currently the sore of the area.
This research has presented suitable sites for waste collection with specifications that enable optimum waste collection. These sites would be 30 meters away from the riparian land (which is in accordance to the Kenyan laws (Environmental Management and Coordination Act 2015) that define riparian land as being a minimum of 6 meters and up to a maximum of 30 meters on either side of a river bank from the highest watermark.), close proximity to roads and road intersections and 10-meter buffer from residential/ built-up regions.
Protection of Riparian lands compound to high water quality, which is a current problem for the Nairobi River passing through the area. Having collection points/ bins near the roads and road intersections would successively lead to saving of fuel costs used by garbage trucks since time used for collection would be minimized.
With a cooperative community, residential associations would come in handy, and subsidized prices for the waste collection could be agreed on.
Properly understanding and assessing a situation is fundamental in giving a proper solution. In this study, the area is visualized in the web application presenting the condition of waste dumping in the area.
Overlain with a raster layer(suitability map) that is spatially aligned (co-registered), covering identical areas with the vector ones while maintaining equal resolution is an added asset for the system. Combination of this information, therefore, can aid in locating the appropriate waste collection points and procedures in the sub location.
A routing system found in the application would also enable saving of fuel costs used by garbage trucks since time used for collection would be minimized. This is because it not only suggests the shortest but also the best routes for navigation.
An integral part of the application is on the interaction of different users to show accountability on collection, transportation, recycling and dumping of waste. This is due to the fact that it proposes incorporation of municipal administrators, transporters/ collectors, recyclers, residents and the landfill management in the entire process, actively.
By each of these members giving a feedback/ report, the whole process can be controlled, efficient and effective. A manual method of recording has been in use where information on the waste collection is recorded in a book.
This research aims to improve on the efficiency of the system since the information entered would be on a real-time basis. This also would lead to reduction of paper-work which would minimize its unnecessary use and waste and in the long run would save our forests; additional costs including financial storage, time and energy costs will also be reduced.





Leave feedback about this